
Tungsten is a rare metallic that occurs naturally on World almost exclusively in chemical compounds. Tungsten is an inherently breakable and hard material, which makes information technology difficult to work.
Protons and Neutrons in Tungsten
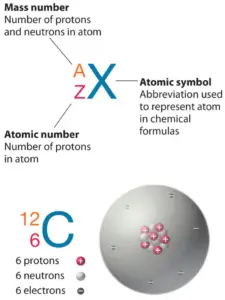 Tungsten is a element with atomic number74 which means there are 74 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called thediminutive number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The full electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals toane,602 x x-xix coulombs.
Tungsten is a element with atomic number74 which means there are 74 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called thediminutive number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The full electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals toane,602 x x-xix coulombs.
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called theneutron number of the atom and is given thesymbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number:N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as theneutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
For stable elements, there is usually a diversity of stable isotopes. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same chemical element, just differ in the number of neutrons. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Tungsten are182-184, 186.
Chief Isotopes of Tungsten
Tungsten occurs in 5 natural isotopes: 180W, 182W, 183Due west, 184W and 186W. 180W is very slightly radioactive, decaying by alpha decay with a half-life of 1.8×1018 years. 184W is the most common isotope, having a natural abundance of approximately 30%.
Tungsten-180 is composed of 74 protons, 106 neutrons, and 74 electrons.
Tungsten-182 is composed of 74 protons, 108 neutrons, and 74 electrons.
Tungsten-183 is equanimous of 74 protons, 109 neutrons, and 74 electrons.
Tungsten-184 is equanimous of 74 protons, 110 neutrons, and 74 electrons.
Tungsten-186 is composed of 74 protons, 112 neutrons, and 74 electrons.
Naturally Occuring Isotopes
| Isotope | Abundance | Neutron Number |
| 180W (unstable) | 0.12% | 106 |
| 182W | 26.l% | 108 |
| 183W | fourteen.31% | 109 |
| 184Westward | 30.64% | 110 |
| 186Westward | 28.43% | 112 |
Electrons and Electron Configuration
The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the aforementioned as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Tungsten is 74. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced past the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the cantlet.
Since the number of electrons and their arrangement are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, theatomic number identifies the diverse chemical elements. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each chemical element's electron shells, particularly the outermost valence beat, is the primary cistron in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing diminutive number Z.
Electron configuration ofTungstenis[Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2.
Possible oxidation states are+6.
Most Common Compound of Tungsten
Tungsten carbides (Westward two C and WC) are produced past heating powdered tungsten with carbon. Approximately half of the tungsten is consumed for the production of hard materials – namely tungsten carbide – with the remaining major use existence in alloys and steels. Mining and mineral processing demand wearable-resistant machines and components, because the energies and masses of interacting bodies are significant. For this purposes, materials with the highest wear-resistance must be used. For example, tungsten carbide is used extensively in mining in top hammer stone drill bits, downhole hammers, roller-cutters, long wall plough chisels, long wall shearer picks, raiseboring reamers, and tunnel irksome machines.
Almost Protons
 A proton is one of the subatomic particles that brand upwardly affair. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upwardalmost one-half of all visible matter. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to ane.67262 × 10−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but almost 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean foursquare radius of nearly 0.87 × x−fifteen m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
A proton is one of the subatomic particles that brand upwardly affair. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upwardalmost one-half of all visible matter. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to ane.67262 × 10−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but almost 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean foursquare radius of nearly 0.87 × x−fifteen m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
The protons exist in the nuclei of typical atoms, along with their neutral counterparts, the neutrons. Neutrons and protons, commonly callednucleons, are bound together in the diminutive nucleus, where they account for 99.nine percent of the atom'south mass. Research in high-free energy particle physics in the 20th century revealed that neither the neutron nor the protonis not the smallest building cake of affair.
About Neutrons
A neutron is one of the subatomic particles that make upwardly affair. In the universe, neutrons are abundant, making upmore half of all visible thing. It hasno electric accuse and a residual mass equal to 1.67493 × 10−27 kg—marginally greater than that of the proton merely well-nigh 1839 times greater than that of the electron. The neutron has a hateful square radius of nigh 0.eight×10−xv m, or 0.8 fm, and it is a spin-½ fermion.
Diminutive nuclei consist of protons and neutrons, which attract each other throughthe nuclear force, while protons repel each other viathe electrical force due to their positive charge. These two forces compete, leading to various stability of nuclei. At that place are only sure combinations of neutrons and protons, which formsstable nuclei.
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus, considering they attract each other and protons , which helps showtime the electrical repulsion between protons. As a result, as the number of protons increases,an increasing ratio of neutrons to protons is needed to form a stable nucleus. If in that location are also many or too few neutrons for a given number of protons, the resulting nucleus is non stable and it undergoes radioactive decay.Unstable isotopesdecay through diverse radioactive decay pathways, most unremarkably blastoff decay, beta decay, or electron capture. Many other rare types of decay, such as spontaneous fission or neutron emission are known. Information technology should exist noted that all of these disuse pathways may be accompanied pastthe subsequent emission of gamma radiations. Pure alpha or beta decays are very rare.
Most Electrons and Electron Configuration
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemic properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Cognition of theelectron configuration of unlike atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic tabular array of elements.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Thechemic properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, past number andorganisation of electrons. Theconfiguration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element'due south electron shells, particularly the outermost valence vanquish, is the chief factor in determining its chemic bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
It is thePauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an cantlet to occupy different energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground land. The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (ground country) and moves progressively from in that location up the energy scale until each of the atom's electrons has been assigned a unique set up of quantum numbers. This fact has key implications for the building up of the periodic table of elements.
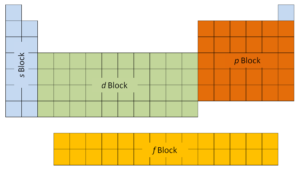 The first 2 columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thes subshells are existence occupied. Because of this, the offset ii rows of the periodic table are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep cakeare the correct-almost vi columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the center 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef blockis the 14-column section that is normally depicted every bit discrete from the principal body of the periodic table. It could be part of the main trunk, just then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
The first 2 columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thes subshells are existence occupied. Because of this, the offset ii rows of the periodic table are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep cakeare the correct-almost vi columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the center 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef blockis the 14-column section that is normally depicted every bit discrete from the principal body of the periodic table. It could be part of the main trunk, just then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy so an abbreviated notation is used. The electron configuration can exist visualized equally the cadre electrons, equivalent to theelement of group 0 of the preceding catamenia, and the valence electrons (e.thousand. [Xe] 6s2 for barium).
Oxidation States
Oxidation states are typically represented by integers which may be positive, zero, or negative. Most elements take more one possible oxidation state. For example, carbon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4.
The current IUPAC Gold Book definition of oxidation state is:
"Oxidation state of an cantlet is the charge of this cantlet later on ionic approximation of its heteronuclear bonds…"
and the term oxidation number is nearly synonymous. An element that is not combined with whatsoever other dissimilar elements has an oxidation state of 0. Oxidation state 0 occurs for all elements – it is simply the chemical element in its elemental form. An atom of an element in a chemical compound will accept a positive oxidation state if it has had electrons removed. Similarly, adding electrons results in a negative oxidation state. We accept likewise distinguish between the possible and common oxidation states of every chemical element. For example, silicon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −iv to +4, but but -4, 0 and +iv are common oxidation states.
Summary
| Element | Tungsten |
| Number of protons | 74 |
| Number of neutrons (typical isotopes) | 182-184, 186 |
| Number of electrons | 74 |
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2 |
| Oxidation states | +6 |

Source: www.luciteria.com
Other backdrop of Tungsten

 Tungsten is a element with atomic number74 which means there are 74 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called thediminutive number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The full electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals toane,602 x x-xix coulombs.
Tungsten is a element with atomic number74 which means there are 74 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called thediminutive number of the atom and is given thesymbol Z. The full electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals toane,602 x x-xix coulombs.

 A proton is one of the subatomic particles that brand upwardly affair. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upwardalmost one-half of all visible matter. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to ane.67262 × 10−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but almost 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean foursquare radius of nearly 0.87 × x−fifteen m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion.
A proton is one of the subatomic particles that brand upwardly affair. In the universe, protons are abundant, making upwardalmost one-half of all visible matter. It hasa positive electric charge (+1e) and a rest mass equal to ane.67262 × 10−27 kg (938.272 MeV/c ii )— marginally lighter than that of the neutron but almost 1836 times greater than that of the electron. The proton has a mean foursquare radius of nearly 0.87 × x−fifteen m, or 0.87 fm, and it is a spin – ½ fermion. The first 2 columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thes subshells are existence occupied. Because of this, the offset ii rows of the periodic table are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep cakeare the correct-almost vi columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the center 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef blockis the 14-column section that is normally depicted every bit discrete from the principal body of the periodic table. It could be part of the main trunk, just then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
The first 2 columns on the left side of the periodic table are where thes subshells are existence occupied. Because of this, the offset ii rows of the periodic table are labeled thesouthward block. Similarly, thep cakeare the correct-almost vi columns of the periodic table, thed blockis the center 10 columns of the periodic table, while thef blockis the 14-column section that is normally depicted every bit discrete from the principal body of the periodic table. It could be part of the main trunk, just then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
0 Response to "Number Of Electrons In Tungsten"
Post a Comment